Aging Cell Q1
 Unclaimed
Unclaimed
Aging Cell is a journal indexed in SJR in Cell Biology and Aging with an H index of 163. It is an CC BY Journal with a Single blind Peer Review review system, and It has a price of 2520 €. The scope of the journal is focused on ageing, longevity, lifespan, apoptosis, gerontology. It has an SJR impact factor of 2,738 and it has a best quartile of Q1. It is published in English. It has an SJR impact factor of 2,738.
Aging Cell focuses its scope in these topics and keywords: human, aging, protein, degeneration, decrement, dehydroalanine, dehydrobutyrine, diseaseepigenomic, downregulation, drivers, ...
Type: Journal
Type of Copyright: CC BY
Languages: English
Open Access Policy: Open Access
Type of publications:
Publication frecuency: -



2520 €
Inmediate OANPD
Embargoed OA- €
Non OAMetrics
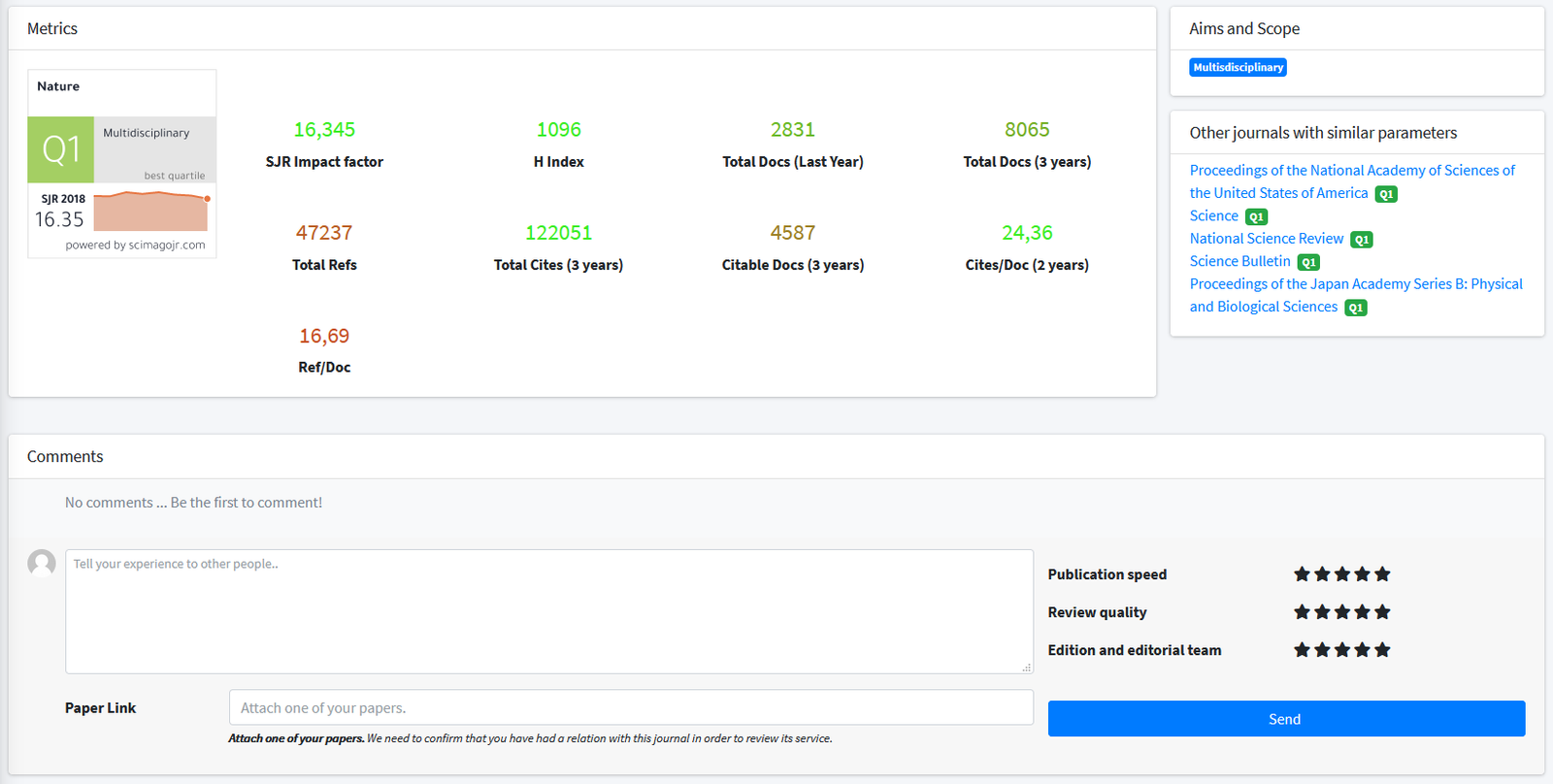
2,738
SJR Impact factor163
H Index199
Total Docs (Last Year)616
Total Docs (3 years)11907
Total Refs5237
Total Cites (3 years)612
Citable Docs (3 years)7.6
Cites/Doc (2 years)59.83
Ref/DocOther journals with similar parameters
Nature Cell Biology Q1
Molecular Cell Q1
Genome Biology Q1
Nature Microbiology Q1
Cell Stem Cell Q1
Compare this journals
Aims and Scope
Best articles by citations
Age-dependent change in reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide generation by rat alveolar macrophages*
View moreRebuttal to Hasty and Vijg: 'Accelerating aging by mouse reverse genetics: a rational approach to understanding longevity'
View moreSenescence rates in patients with end-stage renal disease: a critical appraisal of the Gompertz model
View moreSpecific suppression of insulin sensitivity ingrowth hormone receptorgene-disrupted (GHR-KO) mice attenuates phenotypic features of slow aging
View moreCommentary on 'Fast anterograde transport of Herpes Simplex Virus: Role for the amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer's disease' by Prasanna Satpute-Krishnan et al. Aging Cell Vol. 2, Issue 6, 305-318 (2003)
View moreAccelerated aging-related transcriptome changes in the female prefrontal cortex
View moreLoss of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A extends lifespan in mice
View moreMuscle precursor cells isolated from aged rats exhibit an increased tumor necrosis factor-a response
View moreLifespan extension by increased expression of the Drosophila homologue of the IGFBP7 tumour suppressor
View moreMetal Ions and Neurodegenerative Diseases Paolo Zatta, Editor. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd, Singapore, 2004, pp 400
View moreModellingin vivoskeletal muscle ageingin vitrousing three-dimensional bioengineered constructs
View moreSpecial Issue: Mitochondria and Aging - Facts and Fancies
View moreAlzheimer-related protein APL-1 modulates lifespan through heterochronic gene regulation in Caenorhabditis elegans
View moreSir2 deletion prevents lifespan extension in 32 long-lived mutants
View moreIntroduction
View moreA genetic interaction between RAP1 and telomerase reveals an unanticipated role for RAP1 in telomere maintenance
View moreEffects of IGF-1 isoforms on muscle growth and sarcopenia
View moreSuperoxide-lowering therapy with TEMPOL reverses arterial dysfunction with aging in mice
View moreAdvanced oxidation protein products induce pre-osteoblast apoptosis through a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-dependent, mitogen-activated protein kinases-mediated intrinsic apoptosis pathway
View moreDysfunction of the unfolded protein response increases neurodegeneration in aged rat hippocampus following proteasome inhibition
View moreIntroduction
View moreBorn this way: Hippocampal neurogenesis across the lifespan
View moreShort-term starvation stress at young adult stages enhances meiotic activity of germ cells to maintain spermatogenesis in aged male
View moreEpigenetic gambling and epigenetic drift as an antagonistic pleiotropic mechanism of aging
View more
 If you are a journal editor you can claim the journal profile and add new information for the visitors.
If you are a journal editor you can claim the journal profile and add new information for the visitors.
Comments