
ISSN: 0892-6638
Journal Home
Journal Guideline
FASEB Journal Q1 Unclaimed
FASEB Journal is a journal indexed in SJR in Molecular Biology and Medicine (miscellaneous) with an H index of 297. It has an SJR impact factor of 1,386 and it has a best quartile of Q1. It is published in English. It has an SJR impact factor of 1,386.
FASEB Journal focuses its scope in these topics and keywords: human, protein, receptor, cell, expression, cells, induced, dna, signaling, implications, ...
Type: Journal
Type of Copyright:
Languages: English
Open Access Policy:
Type of publications:
Publication frecuency: -


- €
Inmediate OANPD
Embargoed OA- €
Non OAMetrics
1,386
SJR Impact factor297
H Index574
Total Docs (Last Year)3120
Total Docs (3 years)31176
Total Refs14965
Total Cites (3 years)3083
Citable Docs (3 years)4.45
Cites/Doc (2 years)54.31
Ref/DocOther journals with similar parameters
Molecular Cell Q1
Annual Review of Plant Biology Q1
Cell Research Q1
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology Q1
Nature Protocols Q1
Compare this journals
Aims and Scope
Best articles by citations
Senescence of human skeletal muscle impairs the local inflammatory cytokine response to acute eccentric exercise
View moreFactors limiting autogene-based cytoplasmic expression systems
View moreBone marrow stem cells have the ability to populate the entire central nervous system into fully differentiated parenchymal microglia
View moreA maternal blood-borne factor promotes survival of the developing thalamus
View moreEndothelial cell modulation of bone marrow stromal cell osteogenic potential
View moreHeme oxygenase-1 modulates the allo-immune response by promoting activation-induced cell death of T cells
View moreThe proinvasive activity of Wnt-2 is mediated through a noncanonical Wnt pathway coupled to GSK-3beta and c- Jun/AP-1 signaling
View moreTransducible heat shock protein 20 (HSP20) phosphopeptide alters cytoskeletal dynamics
View moreHO-1 induction restores c-AMP-dependent lung epithelial fluid transport following severe hemorrhage in rats
View moreCaloric restriction attenuates beta-amyloid neuropathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
View moreRepetitive postprandial hyperglycemia increases cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury: prevention by the a-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose
View moreConversion of a scorpion toxin agonist into an antagonist highlights an acidic residue involved in voltage sensor trapping during activation of neuronal Na
View moreFunctional genomic analysis of the ADP-ribosylation factor family of GTPases: phylogeny among diverse eukaryotes and function in
View moreJust lip prints? No: there could be something else
View moreInhibition of host connective tissue growth factor expression: a novel
View moreFormation of amyloid aggregates from human lysozyme and its disease-associated variants using hydrostatic pressure
View moreMolecular basis of the mammalian potency of the scorpion a-like toxin, BmK M1
View morePeroxynitrite induces senescence and apoptosis of red blood cells through the activation of aspartyl and cysteinyl proteases
View moreIsoprostanes: markers and mediators of oxidative stress
View moreRef-1/Ape is critical for formation of the hypoxia-inducible transcriptional complex on the hypoxic response element of the rat pulmonary artery endothelial cell VEGF gene
View moreThe arachidonic acid-binding protein S100A8/A9 promotes NADPH oxidase activation by interaction with p67
View moreThe wild-type Ras: road ahead
View moreApoptotic adaptations from exercise training in skeletal and cardiac muscles
View moreToll-like receptor 4 functions intracellularly in human coronary artery endothelial cells: roles of LBP and sCD14 in mediating LPS-responses
View more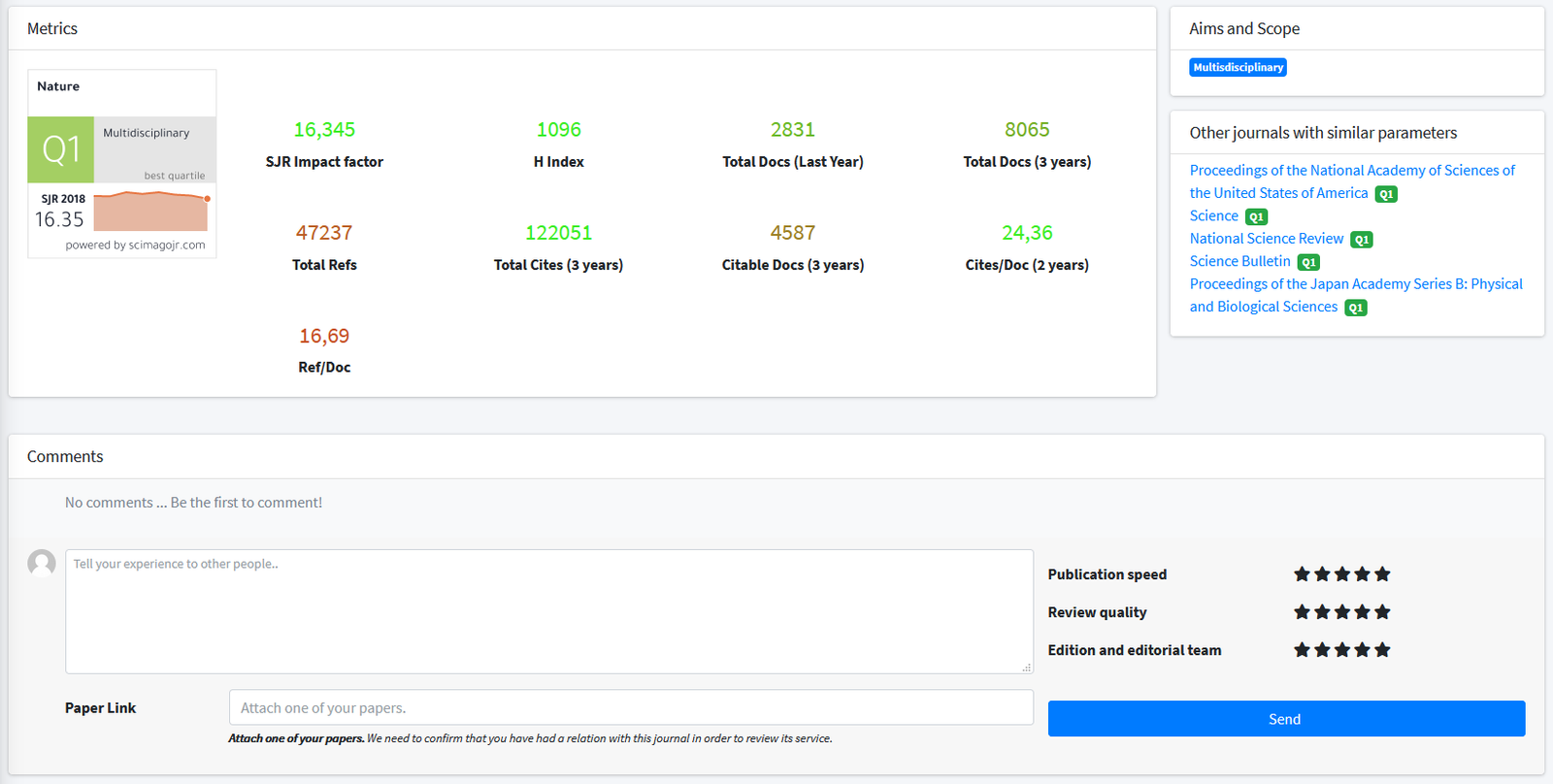 If you are a journal editor you can claim the journal profile and add new information for the visitors.
If you are a journal editor you can claim the journal profile and add new information for the visitors.
Comments