
ISSN: 1350-0872
Journal Home
Journal Guideline
Microbiology Q2 Unclaimed
Microbiology is a journal indexed in SJR in Microbiology with an H index of 194. It has an SJR impact factor of 0,725 and it has a best quartile of Q2. It is published in English. It has an SJR impact factor of 0,725.
Microbiology focuses its scope in these topics and keywords: gene, bacillus, escherichia, expression, coli, cell, growth, synthase, protein, activity, ...
Type: Journal
Type of Copyright:
Languages: English
Open Access Policy:
Type of publications:
Publication frecuency: -


- €
Inmediate OANPD
Embargoed OA- €
Non OAMetrics
0,725
SJR Impact factor194
H Index150
Total Docs (Last Year)374
Total Docs (3 years)9800
Total Refs990
Total Cites (3 years)338
Citable Docs (3 years)2.28
Cites/Doc (2 years)65.33
Ref/DocOther journals with similar parameters
Cellular Microbiology Q2
Microbes and Infection Q2
Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology Q2
BMC Microbiology Q2
Microorganisms Q2
Compare this journals
Aims and Scope
Best articles by citations
Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin alters growth, activity and cell envelope features of sterol-transforming mycobacteria
View moreSeptal Sealing in the Basidiomycete Coriolus versicolor
View moreAn aspartic proteinase gene family in the filamentous fungus Botrytis cinerea contains members with novel features
View moreAutophosphorylation of Yeast Hexokinase PII
View moreAlteration Of Susceptibility To Edta, Polymyxin B And Gentamicin In Pseudomonas Aeruginosa By Divalent Cation Regulation Of Outer Membrane Protein H1
View moreA Correlation between Mode of Growth and Regional Ultrastructure of the Plasma Membrane of Schizosaccharomyces pombe as Revealed by Freeze-fracturing before and after Filipin Treatment
View moreEvidence for Plasmid-mediated Restriction-Modification in Mycobacterium avium intracellulare
View moreUnique expression of a highly conserved mycobacterial gene in IS901
View moreAllosteric NADP-glutamate dehydrogenase from aspergilli: purification, characterization and implications for metabolic regulation at the carbon-nitrogen interface
View moreA Comparison of Phospholipase Activity, Cellular Adherence and Pathogenicity of Yeasts
View moreLocalization of Chitin Synthase in Mucor rouxii by an Autoradiographic Method
View moreUptake of Galactose and Lactose by Kluyveromyces lactis: Biochemical Characteristics and Attempted Genetical Analysis
View morePCR-based identification of zoonotic isolates of Blastocystis from mammals and birds
View morePhospholipase D activity is required for dimorphic transition in Candida albicans
View moreMethods for Selection of Mutants and In Vitro Culture of Cochliobolus heterostrophus
View moreThe Association Between a Large Molecular Mass Plasmid and Virulence in a Strain of Salmonella pullorum
View moreCarbapenems as inhibitors of OXA-13, a novel, integron-encoded -lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
View moreCarnitine acetyltransferases are required for growth on non-fermentable carbon sources but not for pathogenesis in Candida albicans
View moreUltrastructure of Bacilli and the Bacillary Origin of the Macrophagic Inclusions in Whipple's Disease
View moreThe immunogenicity of recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis bearing BCG genes
View moreThe Identification of Antigenic Determinants on Mycobacterium bovis Using Monoclonal Antibodies
View moreThe bacterial microbiota in the oral mucosa of rural Amerindians
View moreTemporal and Spatial Differences in Cell Wall Expansion during Bud and Mycelium Formation in Candida albicans
View moreTritrichomonas foetus and Trichomonas vaginalis: the pattern of inactivation of hydrogenase activity by oxygen and activities of catalase and ascorbate peroxidase
View more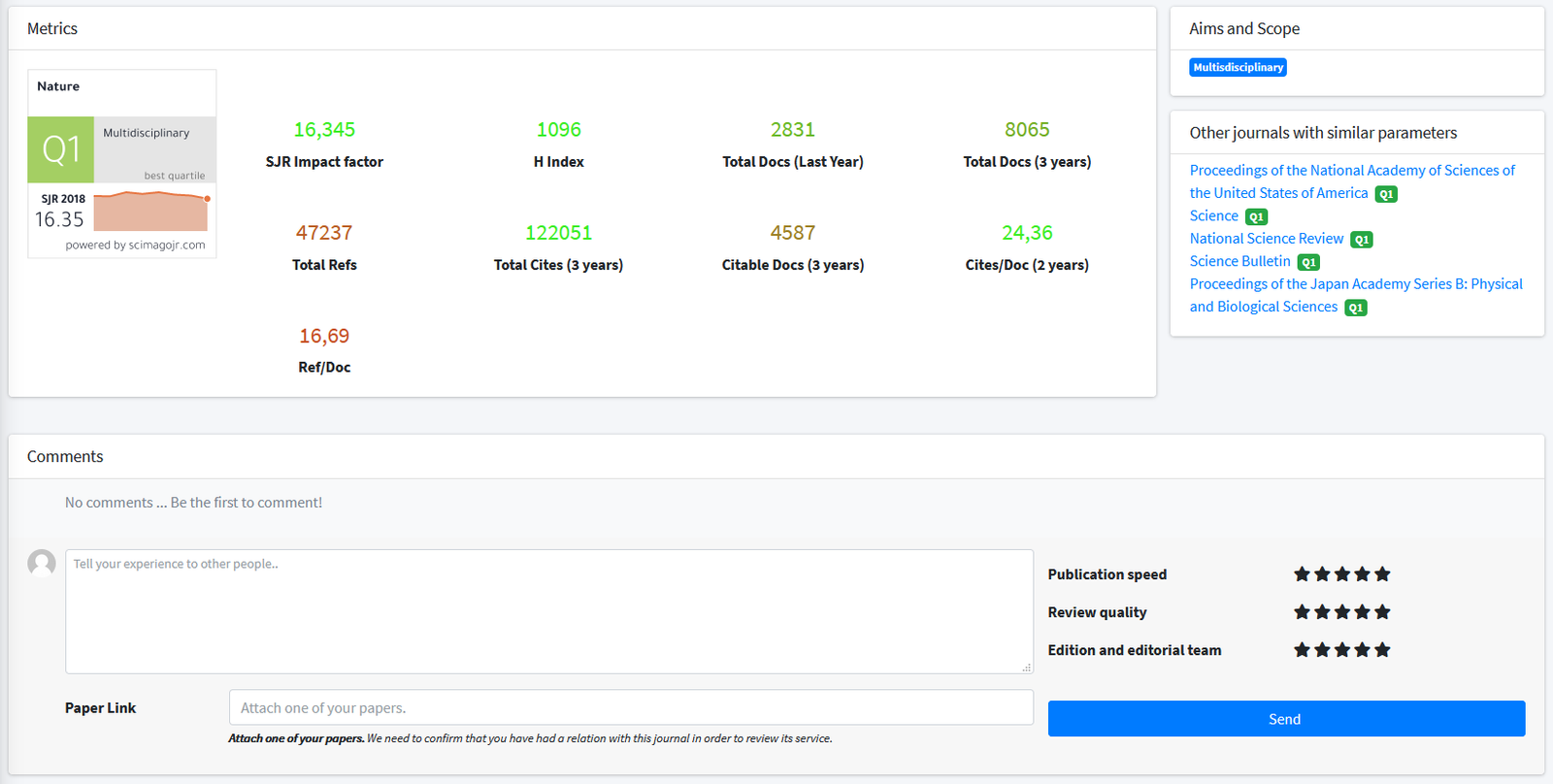 If you are a journal editor you can claim the journal profile and add new information for the visitors.
If you are a journal editor you can claim the journal profile and add new information for the visitors.
Comments